Catalogue
Rabbit anti Farnesyl
Catalog number: X1165P| Isotype | IgG |
| Product Type |
Polyclonal Antibody |
| Units | 100 µg |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Species Reactivity |
Ubiquitous |
| Application |
ELISA Immunofluorescence |
Background
Protein isoprenylation is a post-translational modification that affects about 0.5% of cellular proteins and is essential for the biological activity of proteins. Two enzymes catalyze the attachment of two prenyl groups to the sulfhydryl group of carboxyl-terminal cysteine groups. Proteins which are prenylated by these enzymes have a distinct motif at the C-terminal of the protein, C-A1-A2-X (C = Cysteine, A1 & A2 = aliphatic amino acids). The two enzymes involved in this transfer are farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase. These transfer a 15 carbon farnesyl or a 20 carbon geranygeranyl, respectively, from a prenyl-pyrophosphate to the protein. Examples of proteins containing this C-A-A-X motif are members of the Ras small G protein family, the nuclear lamins and the gamma subunit of trimeric G proteins. Prenylation of proteins is necessary for membrane association of proteins as well as protein-protein interactions and the nature of the linked isoprenyl group can influence the protein interactions, such as the interaction between G proteins and receptors.
Source
Rabbit immunized with farnesyl cysteine conjugated to KLH.
Product
Product Form: Unconjugated
Formulation: Provided as solution in phosphate buffered saline with 0.08% sodium azide
Purification Method: Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation
Concentration: See vial for concentration
Applications
Optimal concentration should be evaluated by serial dilutions.
Functional Analysis: Western Blotting
Storage
Product should be stored at -20°C. Aliquot to avoid freeze/thaw cycles
Product Stability: See expiration date on vial
Shipping Conditions: Ship at ambient temperature, freeze upon arrival
Caution
This product is intended FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY, and FOR TESTS IN VITRO, not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures involving humans or animals. It may contain hazardous ingredients. Please refer to the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for additional information and proper handling procedures. Dispose product remainders according to local regulations.This datasheet is as accurate as reasonably achievable, but Nordic-MUbio accepts no liability for any inaccuracies or omissions in this information.
References
1. Baron, R., et al. RhoB prenylation is driven by the three carboxyl-terminal amino acids of the protein: evidenced in vivo by an anti-farnesyl cysteine antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11626-11631
2. Lin, H.P. et al. Localization of isoprenylated antigen of hepatitis delta virus by anti-farnesyl antibodies. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 91-96
3. Aspbury, R.A., et al. Isoprenylation of polypeptides in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998, 1392, 265-275
4. Zhang, F.L. & Casey, P.J. Protein prenylation: molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 241-26
5. Gromov, P.S., et al. Identification of isoprenyl modified proteins metabolically labeled with [3H]farnesyl- and [3H]geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate. Electrophoresis 1996, 17, 1728-1733
Protein Reference(s)
Database Name: SwissProt
Accession Number: P14324
Species Accession: Human
Safety Datasheet(s) for this product:
| NM_Sodium Azide |
|
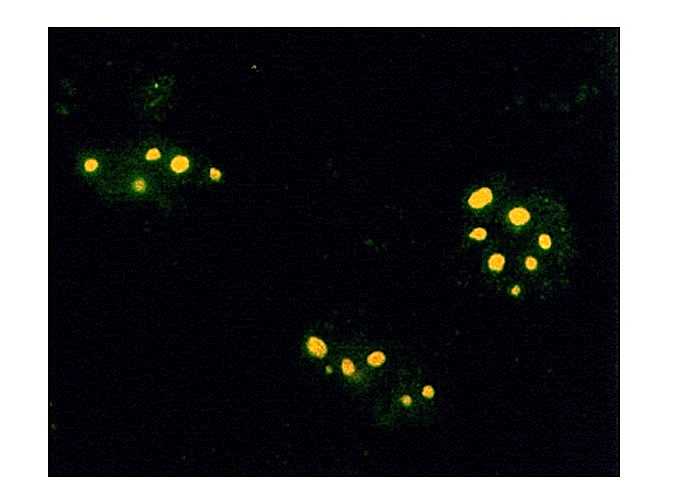
Figure 1. Immunofluorescence assay using anti-Farnesyl antibody on plasmids encoding isoprenylated protein and visualized using FITCconjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody. |

Figure 1. Immunofluorescence assay using anti-Farnesyl antibody on plasmids encoding isoprenylated protein and visualized using FITCconjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody.
