Catalogue
Mouse anti Human CD56
Catalog number: 0561| Clone | C5.9 |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Product Type |
Monoclonal Antibody |
| Units | 250 µg |
| Host | Mouse |
| Species Reactivity |
Human |
| Application |
Flow Cytometry Immunocytochemistry Immunohistochemistry (paraffin) |
Background
NCAM / CD56, as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of adhesion molecules is characterized by several immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains. The extracellular part of NCAM consists of five of these Ig domains and two fibronectin type III homology regions. NCAM is encoded by a single copy gene composed of 26 exons. However, at least 20-30 distinct isoforms can be generated by alternative splicing and by posttranslational modifications, such as sialylation. During sialylation, polysialic acid (PSA) carbohydrates are attached to the extracellular part of NCAM. Through its extracellular region, NCAM mediates homophilic interactions. In addition, NCAM can also undergo heterophilic interactions by binding extracellular matrix components, such as laminin, or other cell adhesion molecules, such as integrins.
NCAM can be found in central and peripheral nerve cells, neuroendocrine tissues and at the surface of NK-cells. Also, NCAM is present in malignancies derived from these tissues and cells.
Synonyms: CD56, NCAM, Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule
Source
Derived from the hybridization of mouse Sp2/0 myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c F1 mice immunized with an extract of the KG1a cell line.
Immunogen: KG1a cell line extract.
Product
Purified monoclonal antibody clone C5.9, filtered, in PBS containing 0.08% azide
Product Form: Unconjugated
Purification Method: ProteinG Chromatography
Concentration: See vial for concentration
Applications
Antibody can be used for Immunohistochemistry (2-5 µg/ml, formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissues). Optimal concentration should be evaluated by serial dilutions.
Functional Analysis: Flow Cytometry
Storage
Product should be stored at -20°C. Aliquot to avoid freeze/thaw cycles
Product Stability: Reagents are stable for the period shown on the vial label when stored properly
Shipping Conditions: Ship at ambient temperature, freeze upon arrival
Caution
This product is intended FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY, and FOR TESTS IN VITRO, not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures involving humans or animals. It may contain hazardous ingredients. Please refer to the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for additional information and proper handling procedures. Dispose product remainders according to local regulations.This datasheet is as accurate as reasonably achievable, but Nordic-MUbio accepts no liability for any inaccuracies or omissions in this information.
References
1. Hercend T., Griffin J.D., Benussan A., Schmidt R.E., Edson M.A., Brennen A., Murray C., Daley J.F., Schlossman S.F., and Ritz J. Generation of Monoclonal Antibodies to a Human Natural Killer Clone. Characterization of Two Natural Killer-Associated Antigens, NKH1 and NKH2, Expressed on Subset of Large Granular Lymphocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 1985,75: 932.
2. Lanier, L.L., Le, A.M., Civin, C.I., Loken, M.R., and Phillips, J.H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) Antigen Expression on Human Peripheral Blood NK Cells and Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986, 136: 4480.
3. Schmidt RE, Murray C, Daley JF, Schlossman SF, and Ritz J, J. A subset of natural killer cells in peripheral blood displays a mature T cell phenotype. J Exp Med 1986, 164: 351-356
4. Caligiuri M, Murray C, Buchwald D, Levine H, Cheney P, Peterson D, Komaroff AL, and Ritz J. Phenotypic and functional deficiency of natural killer cells in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Immunol 1987, 139: 3306-3319
5. Hercend T. and Schmidt R.E. Characteristics and uses of natural killer cells. Immunol Today 1988, 9: 291-293.
6. Muench, Marcus O., et al. Isolation of Definitive Zone and Chromaffin Cells Based upon Expression of CD56 (Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule) in the Human Fetal Adrenal Gland, J Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2003, 88: 3921-3930,
PRODUCT SPECIFIC REFERENCES
1. Horikawa, M., et al. Abnormal Natural Killer Cell Function in Systemic Sclerosis: Altered Cytokine Production and Defective Killing Activity. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2005, 125: 731-737
2. Ishimoto, H., et al. Midkine, a heparin-binding growth factor, selectively stimulates proliferation of definitive zone cells of the human fetal adrenal gland. Journal of Endocrinol. Metab 2006, 91: 4050-4056
3. Muench, M., et al. Isolation of Definitive Zone and Chromaffin Cells Based upon Expression of CD56 (Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule) in the Human Fetal Adrenal Gland. Journal of Clinical Endocrinol. Metab 2003, 88: 3921-3930
4. Miles, L.A., et al. Cell-Surface Actin Binds Plasminogen and Modulates Neurotransmitter Release from Catecholaminergic Cells. Journal of Neuroscience 2006, 26: 13017-13024
Protein Reference(s)
Database Name: UniProt
Accession Number: P13591

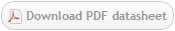
IHC: Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human neuroblastoma stained with Exalpha's CD56, clone C5.9 at 2 ug/ml using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Cell membrane staining of tumor cells is clearly evident. High-temperature heating was used as the retrieval protocol, pressure cooker with citrate buffer, pH 6.5, for 10 min. Exalpha’s anti-CD56,clone C5.9, was added at 2 ug/ml for 1 hour at room temperature followed by anti-Mouse HRP for 30 minutes at room temperature. Staining was visualized using DAB and methyl green counter stain. Flow Cytometry: Flow cytometry data using Exalpha’s Mouse anti Human CD56 antibody 0561 at 8 µg/ml on human lymphocytes, with Rat anti Mouse PE IgG2a & 2b as a second step. The negative control was generated without the CD56 antibody and without the Rat anti Mouse PE IgG2a & 2b. Western Blot: Western blot analysis using Exalpha’s Mouse anti Human CD56 antibody 0561 at 10 µg/ml (left lane) and 1 µg/ml (right lane) showing a strong reaction on recombinant human NCAM-1/CD56 protein.