Catalogue
Mouse anti Vimentin
Catalog number: MUB1902P-CE/IVD| Clone | V9 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Product Type |
Primary Antibodies |
| Units | 0.1 mg |
| Host | Mouse |
| Species Reactivity |
Chicken Human Rat Sheep |
| Application |
Flow Cytometry Immunocytochemistry Immunohistochemistry (frozen) Immunohistochemistry (paraffin) Western Blotting |
Background
Vimentin (57 kDa) is the intermediate filament protein (IFP) of mesenchymal cells. This IFP, often deviates from the tissue-specific and developmentally regulated pattern of expression. Besides its typical expression in most cultured cells, vimentin is also expressed together with several other IFPs during early stages of development. As differentiation proceeds, vimentin is exchanged for the tissue-specific intermediate filament type.
Source
V9 is a Mouse monoclonal IgG1 antibody derived by fusion of PAI Mouse myeloma cells with spleen cells from a BALB/c Mouse immunized with vimentin isolated from porcine lens.
Product
Each vial contains 100 ul 1 mg/ml purified monoclonal antibody in PBS containing 0.09% sodium azide.
Formulation: Each vial contains 100 ul 1 mg/ml purified monoclonal antibody in PBS containing 0.09% sodium azide.
Specificity
V9 reacts exclusively with vimentin, which is expressed in mesenchymal cells and mesenchymal derived tumors e.g. lymphoma, sarcoma and melanoma.
Species Reactivity: Also reacts with potoroo
Applications
V9 is suitable for immunoblotting, immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry on frozen and paraffin-embedded tissues and flow cytometry. For staining paraffin-embedded tissues pretreatment by boiling tissue sections for 10 minutues in 10 mM citRate buffer (pH 6.0) is required. Optimal antibody dilution should be determined by titration; recommended range is 1:25 – 1:200 for flow cytometry, and for immunohistochemistry with avidin-biotinylated Horseradish peroxidase complex (ABC) as detection reagent, and 1:100 – 1:1000 for immunoblotting applications.
Storage
The antibody is shipped at ambient temperature and may be stored at +4°C. For prolonged storage prepare appropriate aliquots and store at or below -20°C. Prior to use, an aliquot is thawed slowly in the dark at ambient temperature, spun down again and used to prepare working dilutions by adding sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2). Repeated thawing and freezing should be avoided. Working dilutions should be stored at +4°C, not refrozen, and preferably used the same day. If a slight precipitation occurs upon storage, this should be removed by centrifugation. It will not affect the performance or the concentration of the product.
Caution
When used for in vitro diagnostic purposes results must be put within the context of other diagnostic tests as well as the clinical history of the patient by a certified professional before final interpretation. Analyses performed with this antibody should be paralleled by positive and negative controls. If unexpected results are obtained which cannot be attributed to differences in laboratory procedures, please contact us. This product may contain hazardous ingredients. Please refer to the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for additional information and proper handling procedures. Dispose product remainders according to local regulations.This datasheet is as accurate as reasonably achievable, but Nordic-MUbio accepts no liability for any inaccuracies or omissions in this information.
References
1. Osborn, M., Debus, E., and Weber, K. (1984). Monoclonal antibodies specific for vimentin, Eur J Cell Biol 34, 137-43.
2. Tolle, H. G., Weber, K., and Osborn, M. (1985). Microinjection of monoclonal antibodies specific for one intermediate filament protein in cells containing multiple Keratins allow insight into the composition of particular 10 nm filaments, Eur J Cell Biol 38, 234-44.
3. Van Muijen, G. N., Ruiter, D. J., and Warnaar, S. O. (1987). Coexpression of intermediate filament polypeptides in Human fetal and adult tissues, Lab Invest 57, 359-69.
4. Van Muijen, G. N., Warnaar, S. O., and Ponec, M. (1987). Differentiation-related changes of Cytokeratin expression in cultured Keratinocytes and in fetal, newborn, and adult epidermis, Exp Cell Res 171, 331-45.
5. Corver, W. E., Koopman, L. A., van der Aa, J., Regensburg, M., Fleuren, G. J., and Cornelisse, C. J. (2000). Four-color multiparameter DNA flow cytometric method to study phenotypic intratumor heterogeneity in cervical cancer, Cytometry 39, 96-107.
6. De Visscher, G., Plusquin, R., Mesure, L., Flameng, W. (2010). Selection of an immunohistochemical panel for cardiovascular research in Sheep. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 18, 382-91.
CE Mark
CE
Safety Datasheet(s) for this product:
| NM_Sodium Azide |

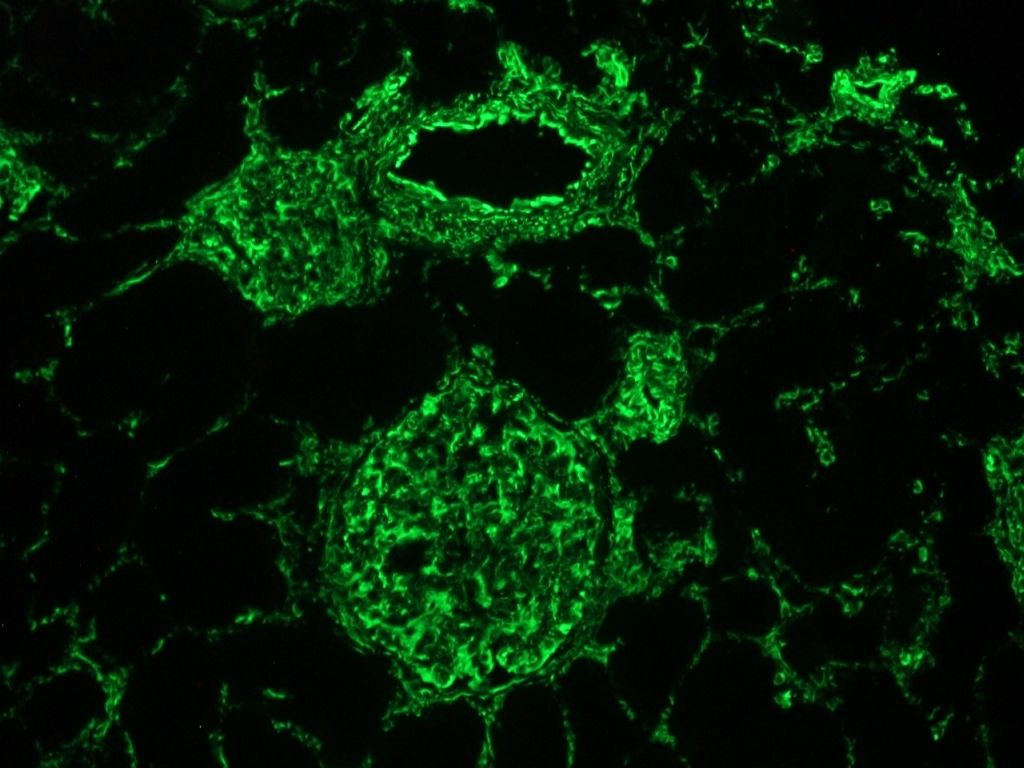
Indirect immunofluorescence staining of human kidney frozen section with MUB1902P (clone V9). Note positive vimentin staining in glomeruli and connective tissue, but not in the epithelial ducts.

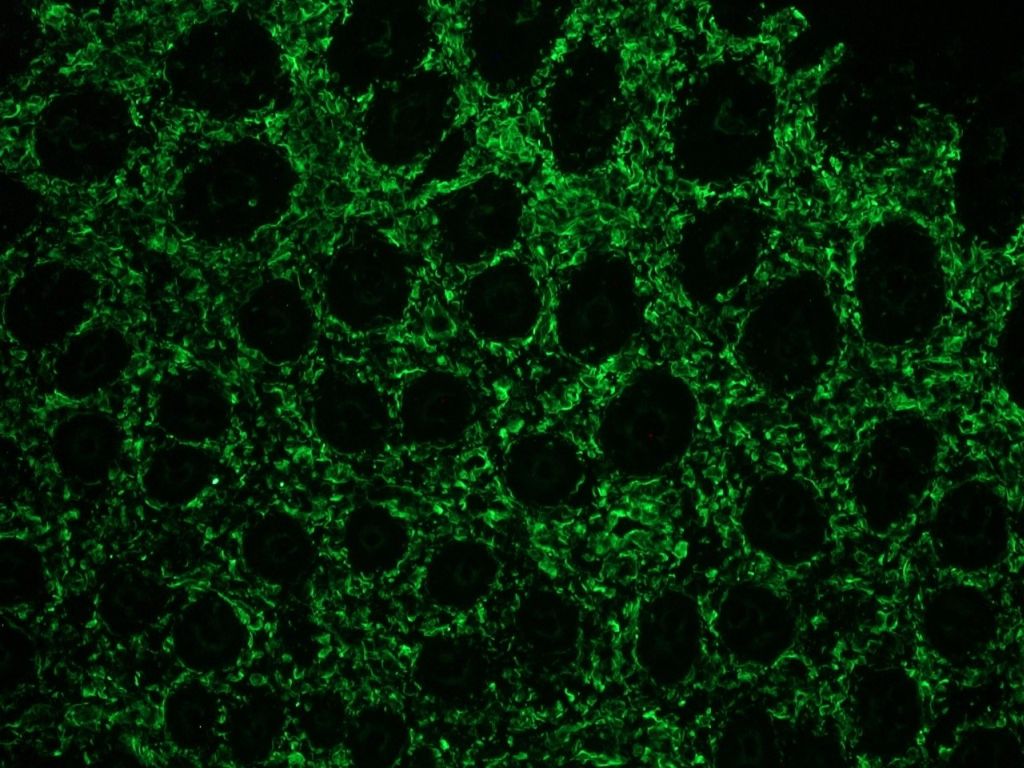
Figure 2. Indirect immunofluorescence staining of swine small intestine frozen section with MUB1902P (clone V9). Note positive vimentin staining in connective tissue, but not in the epithelial cells.

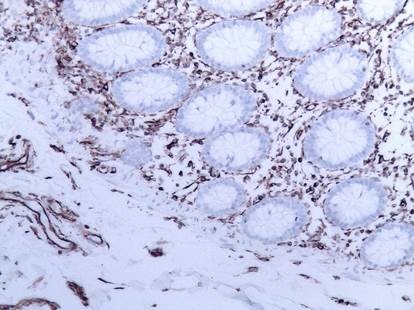
Figure 3. Immunostaining of human small intestine paraffin section with MUB1902P (clone V9). Note positive vimentin staining in connective tissue, but not in the epithelial cells.